From Question Bank
3.)
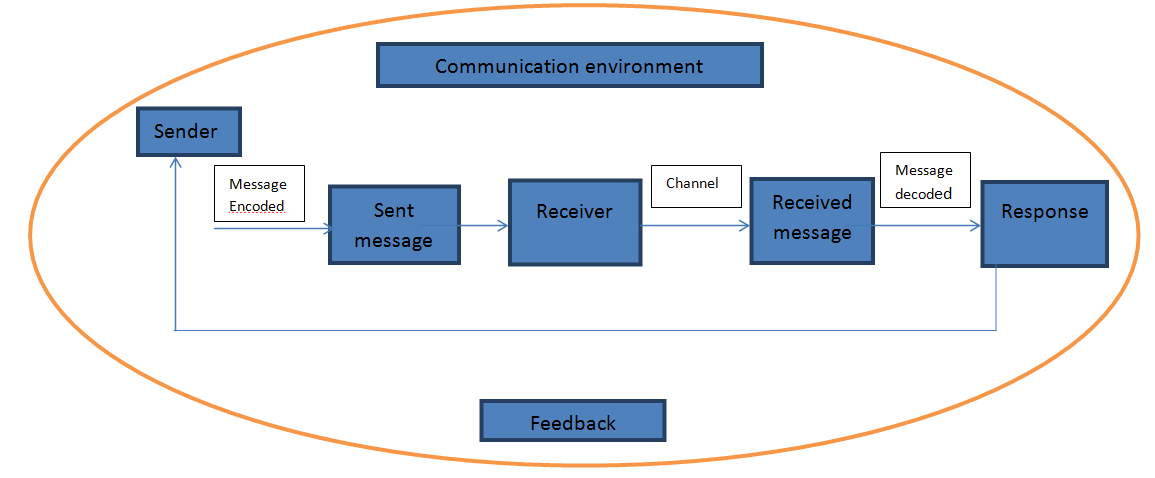
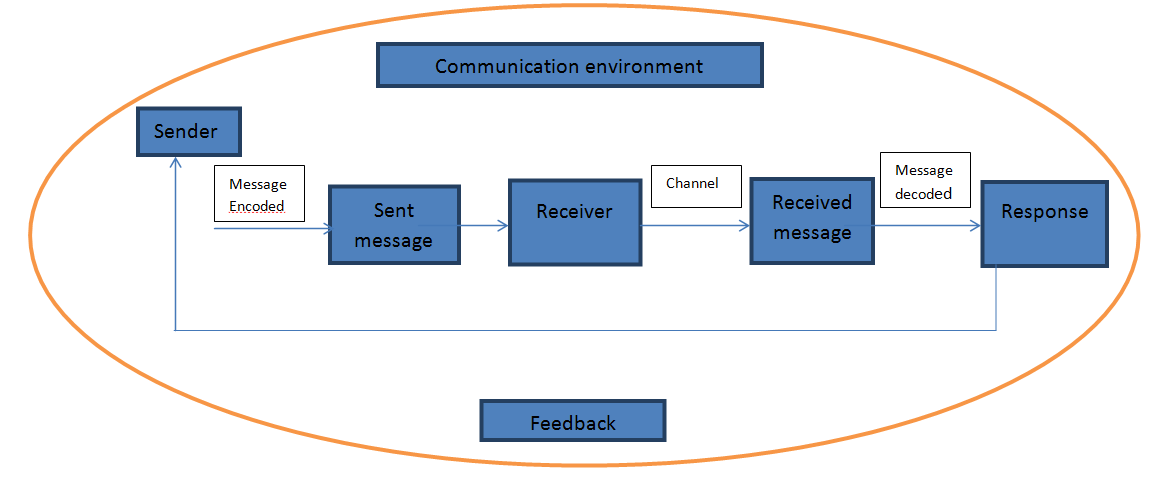
Explain the process of communication with the help of a diagram and mention the
essentials of effective communication (June’11, Nov’10, June’09, Jun’10,
Jan’10)
·
The sender encodes the message and sends it through a
channel. This channel is nothing but the language used-words, actions, signs,
objects or a combination of these.
·
The receiver receives the message, decodes it and acts
on it. If the message received is same as the message sent then there will be a
response and if not there will be a breakdown of communication.
·
The transmission of receiver’s response to the sender
is called ‘feedback’. It is essential for an effective communication.
·
The communication cycle is only complete when you
receive a response from the recipient of the message.
·
Communication takes place in a well-defined set-up,
which is called the ‘communication environment’
Essentials of Effective communication
·
A common communication environment
·
Co-operation between sender and receiver
·
Selection of an appropriate channel
·
Correct encoding and decoding of message
·
Receipt of desired response and feedback
2.) Define communication and explain the process
of communication. Distinguish between general and technical communication.
(Dec’08, Jun’12)
Communication can be defined as the exchange of
information, ideas and knowledge between the sender and receiver through an
accepted code of language
·
The sender encodes the message and sends it through a
channel. This channel is nothing but the language used-words, actions, signs,
objects or a combination of these.
·
The receiver receives the message, decodes it and acts
on it. If the message received is same as the message sent then there will be a
response and if not there will be a breakdown of communication.
·
The transmission of receiver’s response to the sender
is called ‘feedback’. It is essential for an effective communication.
·
The communication cycle is only complete when you
receive a response from the recipient of the message.
·
Communication takes place in a well-defined set-up,
which is called the ‘communication environment’
Difference between general and technical communication
General
Communication
|
Technical
communication
|
Contains
a general message
|
Contains
a technical message
|
Informal
in style and approach
|
Mostly
formal
|
No
set pattern of communication
|
Follows
a set pattern
|
Mostly
oral
|
Can
be written and oral
|
Not
always for a specific audience
|
Always
for a specific audience
|
Doesn’t
involve the use of technical vocabulary or graphic, etc
|
Frequently
involves jargon, graphics etc
|
5.) Distinguish between General and Technical
communication. Explain the importance of Technical communication
7.) Write a detailed note on the need and demand
of Technical communication in global world (write the second
part of this after the difference)
General
Communication
|
Technical
communication
|
Contains
a general message
|
Contains
a technical message
|
Informal
in style and approach
|
Mostly
formal
|
No
set pattern of communication
|
Follows
a set pattern
|
Mostly
oral
|
Can
be written and oral
|
Not
always for a specific audience
|
Always
for a specific audience
|
Doesn’t
involve the use of technical vocabulary or graphic, etc
|
Frequently
involves jargon, graphics etc
|
·
Technical communication plays a vital
role in an organization, whether it is business enterprise, an industry or an
academic institution
·
Communication serves as an instrument
to measure the success or growth of an organization
eg: When a CEO of a company presents
his company’s achievements in a meeting, each of the participants come to know
of these milestones.
·
The various types of communication
not only help an organization to grow, but also enable the communicators to
develop certain attributes
·
Technical communication can be
divided into two groups: Oral and Written
Oral Forms
|
Written Forms
|
Face
to face/ Telephonic conversations
|
Memos,
Letters
|
Meetings/
Seminars
|
E-mails,
Faxes
|
Conferences
|
Circulars,
Newsletters
|
Presentations
|
Reports
|
Group
discussions
|
Proposals
|
Interviews
|
Bulletins,
Brochures
|
Video
/ Voice conferences
|
Manuals,
In-house Journals
|
·
If an organization is large, it may
all these types of communication, whereas a smaller organization may not have
all forms
·
It is the communication which helps
the employees to work together
·
It is the vehicle through which the
organization performs all its functions. Hence its importance cannot be ignored
9.) Discuss the main elements/ components of
non-verbal communication. (Jan’11, Sep’09, Dec’08)
Kinesics
Kinesics
is the name given to the study of the body’s physical movements. It is the way
the body communicates without words
1.)
Personal appearance
It
plays an important role in communication. People see you before they hear you.
As you adapt your language to the audience, you should also dress
appropriately. Appearances communicate how we feel about ourselves and how we
want to be viewed.
2.)
Posture
Posture
refers to the way we hold ourselves when we stand, sit or walk. What one speaks
is important but what you do just before you begin and after you have finished
is equally important.
3.)
Gesture
Gesture
is the movement made by hands, arms, head and torso. A well-timed gesture adds
an impact and greater value to what is being said. Gestures clarify your ideas
4.)
Facial expression
The
face is said to be the most important part of your body. Facial expressions can
be used to aid or inhibit or complement you communication
5.)
Eye contact
The
eyes are considered to be the windows of the soul. You look into the eyes of
the speaker to help find out the truthfulness of his speech, his intelligence,
attitudes and feelings.
Proxemics
It is
the study of physical space in interpersonal relations. The way people use
space tells a lot about them.
Edward
T Hall has divided space into four zones:
1.)Intimate: Personal touch
upto 18 inches (eg: a handshake or a pat on the back or a hug)
2.)Personal: 18 inches to 4
feet( eg: Communication with your friends, colleagues or peers)
3.)Social: 4 feet to 12 feet
(eg: Official communication)
4.)
Public: 12 feet to 30 feet (eg: Public figures like Prime minister communicate
with public)
Paralinguistics
Paralinguistic
features are non-verbal cues that help you to give urgency to your voice.
Voice
adds extra life to your delivery
1.)
Quality
It is
a characteristic that distinguishes one voice from another. While the quality
of voice cannot be changed, but it can be trained for optimum impact
2.)
Volume
It is
the loudness or softness of voice. You should vary your volume so as to make
your voice audible and clear
3.)
Pace/Rate
It is
the number of words which we speak per minute. The normal rate is 120 to 150
words per minute.
4.)
Pitch
It
refers to the number of vibrations per second of your voice. The rise and fall
of voice conveys various emotions
5.)
Articulation
It
means speaking all the sounds distinctly. Speakers should be careful not to
slop, chop, truncate or omit sounds between words or sentences.
6.)
Pronunciation
It
requires speaking out words in a way they are generally accepted
7.)
Voice modulation
It refers
to the way we regulate, vary or adjust the tone, pitch and volume of the sound
or speaking voice. It brings flexibility and vitality to your voice
8.)
Pauses
A
pause is a short silence flanked by words.
10.
Discuss the impact of body language in making a presentation effective (Jun’09)
When a speaker presents
himself, we see him before we start hearing him. Immediately, we begin
developing impressions of his abilities and attitudes based on non-verbal
signals he sends. This is why body language is so critical in oral
communication.
Body language includes every
aspect of your appearance, from what you wear, how you stand, look, and move,
to your facial expressions and physical habits such as nodding your head,
jingling change in your pocket or pulling your necktie. Your use of space and
gestures are other key concerns.
1.)
Personal appearance
It
plays an important role in communication. People see you before they hear you.
As you adapt your language to the audience, you should also dress appropriately.
You should be clean groomed, conforming to the need of the occasion. Appearances
communicate how we feel about ourselves and how we want to be viewed.
2.)
Posture
Posture
refers to the way we hold ourselves when we stand, sit or walk. What one speaks
is important but what you do just before you begin and after you have finished
is equally important.
Slumped
posture- low spirits
Erect
posture- high spirits, energy and confidence
Lean
forward- Open, honest and interested
Lean
backward- Defensive and disinterested
3.)
Gesture
Gesture
is the movement made by hands, arms, head and torso. A well-timed gesture adds
an impact and greater value to what is being said. Gestures clarify your ideas
4.)
Facial expression
The
face is said to be the most important part of your body. Facial expressions can
be used to aid or inhibit or complement you communication
5.)
Eye contact
The
eyes are considered to be the windows of the soul. You look into the eyes of
the speaker to help find out the truthfulness of his speech, his intelligence,
attitudes and feelings.
No comments:
Post a Comment